Alkanoic Acids (carboxylic Acids)
Alkanoic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxylic acid functional group (–COOH). Their general molecular formula is CnH2n+1COOH. They are commonly found in fats and oils.
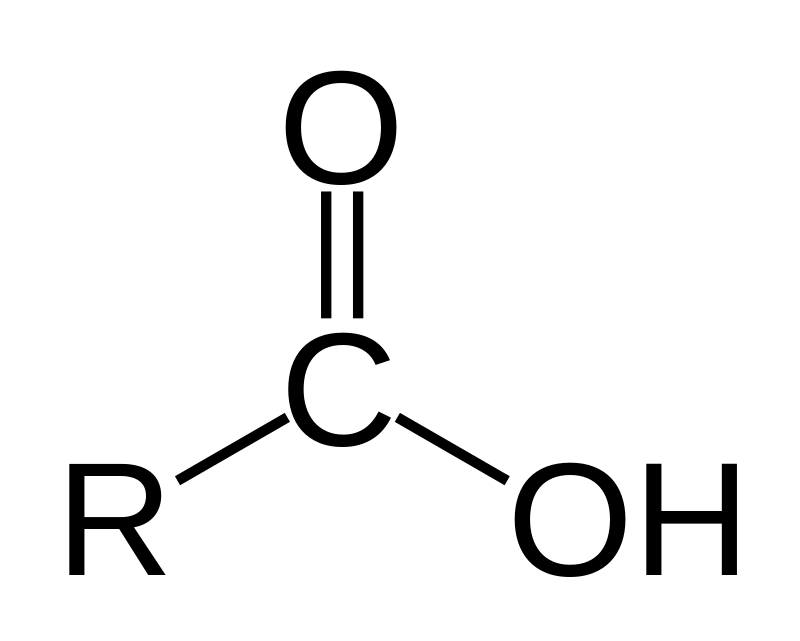 Credit: Wikipedia
Credit: Wikipedia
Examples of Alkanoic Acids
- Methanoic acid (Formic acid): HCOOH – found in insect bites
- Ethanoic acid: CH3COOH
- Propanoic acid: CH3CH2COOH
Preparation
Alkanoic acids can be prepared in the laboratory by oxidizing primary alkanols using excess acidified potassium tetraoxomanganate (VII).
Physical Properties
- Colourless liquid with a sharp, pungent smell
- Sour taste
- Soluble in water
- Freezes into ice-like crystals below 17°C; thus known as glacial ethanoic acid (anhydrous ethanoic acid)
- Boiling point of 118°C
- Turns blue litmus paper red
Chemical Properties
- Reacts with carbonates or hydrogen carbonates to release carbon
dioxide:
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 - Reacts with reactive metals like Ca or Mg to liberate hydrogen
gas:
2CH3COOH + Ca → (CH3COO)2Ca + H2 - Neutralizes bases (alkalis) to form salt and water:
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O - Reacts with alkanols to form esters (esterification):
CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH ⇌ CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O - Reduction: Reduced to ethanol using lithium
tetrahydridoaluminate(III) (LiAlH4):
CH3COOH + 4[H] → CH3CH2OH + H2O - Successive reaction with chlorine to form chlorinated ethanoic
acids:
CH3COOH + Cl2 → CH2ClCOOH + HCl
CH2ClCOOH + Cl2 → CHCl2COOH + HCl
CHCl2COOH + Cl2 → CCl3COOH + HCl
Classification of Alkanoic Acids
- Monocarboxylic Acids: Contain one carboxylic group per molecule (e.g., Methanoic acid - HCOOH)
- Dicarboxylic Acids: Contain two carboxylic groups per molecule (e.g., Ethan-1,2-dioic acid or oxalic acid)
- Tricarboxylic acids: these have 3 carboxylic acid per molecule (e.g. 2-hydroxy propan 1,2, 3, tricaboxylic acid)
Uses of Ethanoic Acid
- Used in making compounds such as cellulose ethanoate and dyes
- Serves as an organic solvent
- Used in the food industry for preservation and flavoring
- Used in coagulating rubber latex